|
Characterizations and applications of nanomaterials |
|||||
High-efficiency photo-electron conversion devices Semiconductor processes and nanofabrication Characterizations and applications of nanomaterials Optical characterization of graphene Graphene-gold oxide photodetector Optical analysis of hollow gold nanoparticles Photomodification of hollow gold nanoparticles for high-density data storage Light harvesting and light extraction Light extraction efficiency of LEDs Antireflection structures for solar cells Optical analysis techniques Eco-friendly devices and sensors
|
Using patterned carbon nanotube films with optical anisotropy to tune the diffracted color from flexible substrates We combine transverse electric (TE) and transverse magnetic (TM) polarized light of various incident angles with optical thin film theory to investigate the optical anisotropy of carbon nanotube (CNT) films. We also determined the relationship between the optical anisotropy and diffraction phenomena in grating-patterned CNT films. For TE polarized light, the diffraction intensity remains almost unchanged upon varying the incident angle. For TMpolarized light, however, the diffraction intensity decreases upon increasing the angle of incidence. We deform and bend flexible substrates to induce dynamic modulation of the diffraction colors from the CNT gratings. Convex bending of the surface increases the period of the CNT gratings, thereby causing more penetration of diffracted light; concave bending decreases the period of the CNT gratings, causing the diffracted light to weaken in intensity in the CNT forest. |
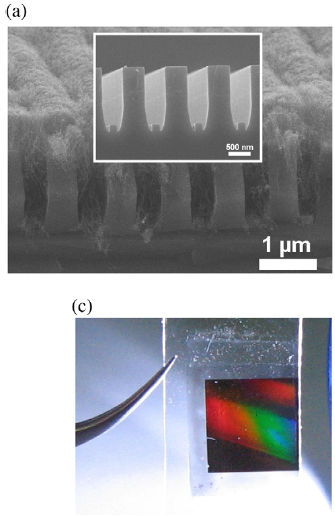
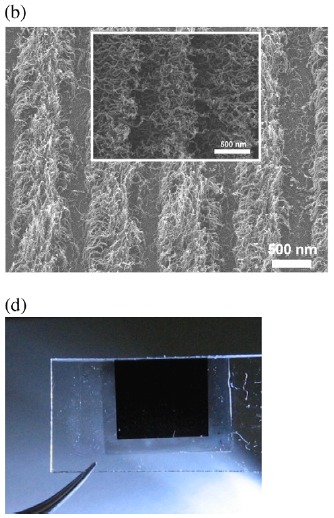
(a and b) SEM images of (a) CNTs grown on a grating-patterned Si substrate (inset: Si template) and (b) CNT gratings transferred to a PC substrates before (inset) and after performing the adhesion and lift-off process. (c and d) Photographs of CNT gratings irradiated with light propagating along the plane-of-incidence (c) perpendicular and (d) parallel to the grating direction.
|
|||
Copyright(c) 2008 Nano-optpelectronics Lab., Department of Material Science and Engineering, National Taiwan University No. 1, Sec. 4, Roosevelt Road, Taipei, 10617 Taiwan(R.O.C) Phone:+886-2-3366-3240 Fax:+886-2-2362-7651 |
|||||